Step 1 – Installing Erlang
RabbitMQ requires Erlang to be installed on the system. So first of all, You can simply download the erlang repository package from its official website and install it on your system. Run the following commands to update the Apt cache and install Erlang packages.
Step 2 – Install RabbitMQ Server
After installing the requirements, now enable RabbitMQ apt repository on your system. Also, you need to import rabbitmq signing key on your system. Use the following commands to do this. After that update the apt cache and install the RabbitMQ server on your system.
Step 3 – Manage RabbitMQ Service
RabbitMQ has been installed on the Debian system. Use the following commands to enable the RabbitMQ service on your system. Also, start the RabbitMQ service.
Step 4 – Create Admin User in RabbitMQ
By default, rabbitmq creates a user named “guest” with the password “guest”. You can also create your own administrator account on the RabbitMQ server using the following commands. Change your password with your own password.
Step 5 – Setup RabbitMQ Web Management Console
RabbitMQ also provides and web management console for managing the entire RabbitMQ. To enable the web management console run the following command on your system. The web management console helps you for managing the RabbitMQ server. RabbitMQ dashboard starts on port 15672. Access your server on the port to get the dashboard. Use the username and password created in step 4
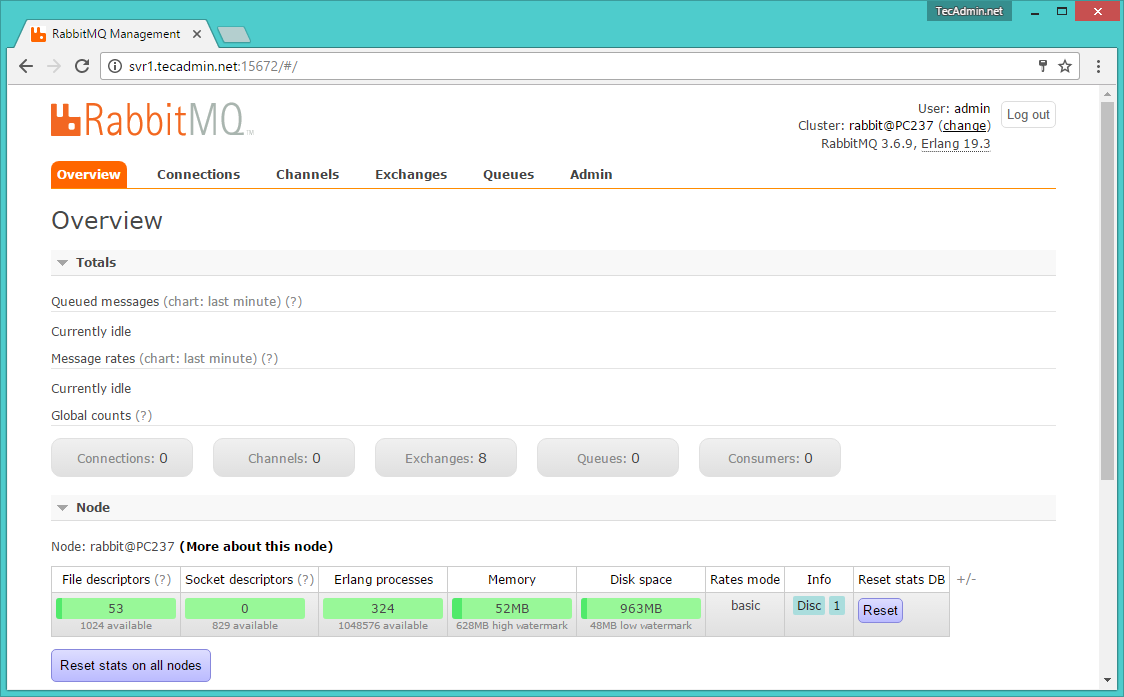
After log in, you will get the RabbitMQ management web interface dashboard.